CSS positions property can help you set the position of the element in the HTML. it is a very useful property and often quite confusing for beginners so I tried to make things easy today!
let's look at the different types of position properties in CSS.
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
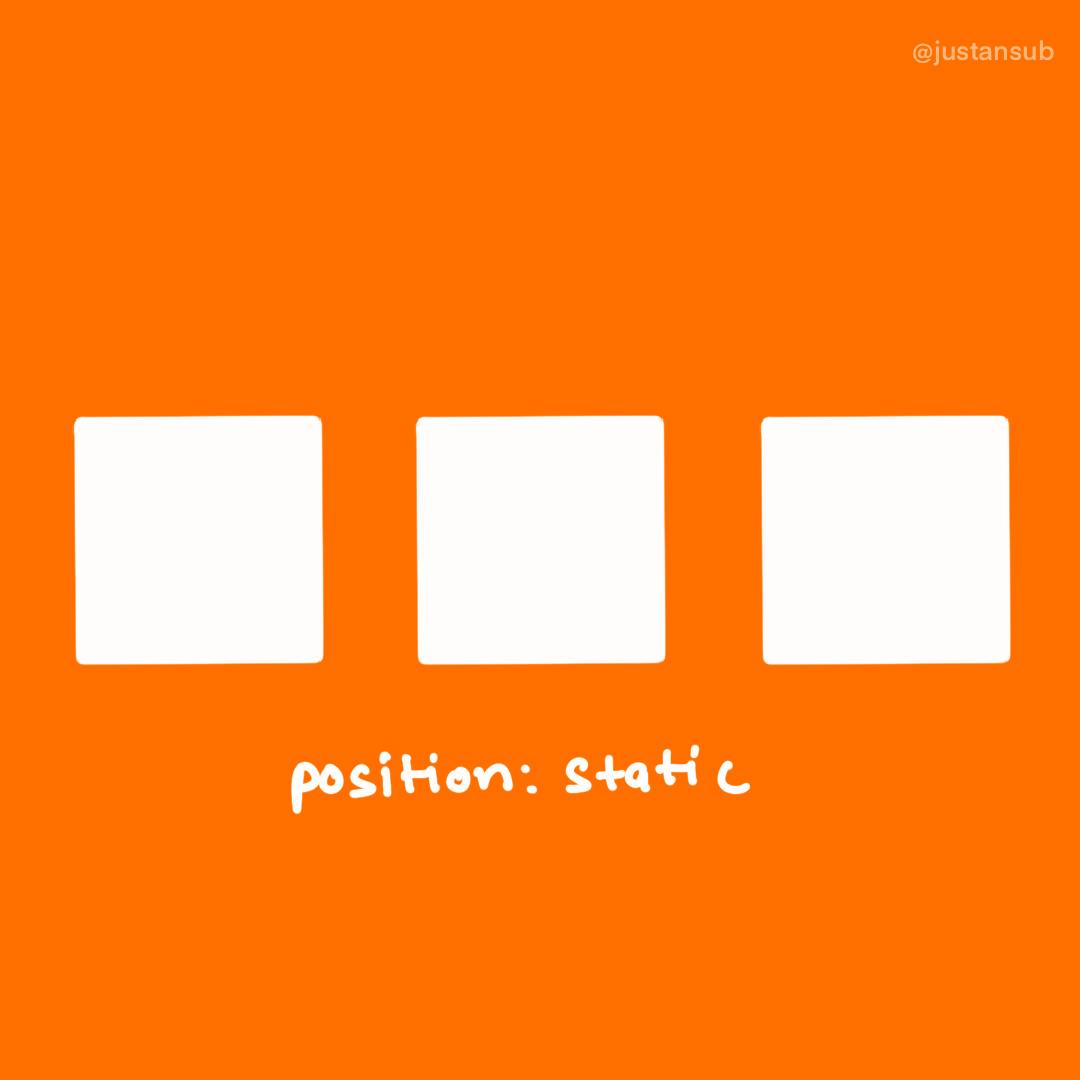
Static
- it is the default for every element
- it means that the element will flow into the page as it normally would.
- use it to remove the forcefully applied position to the element.
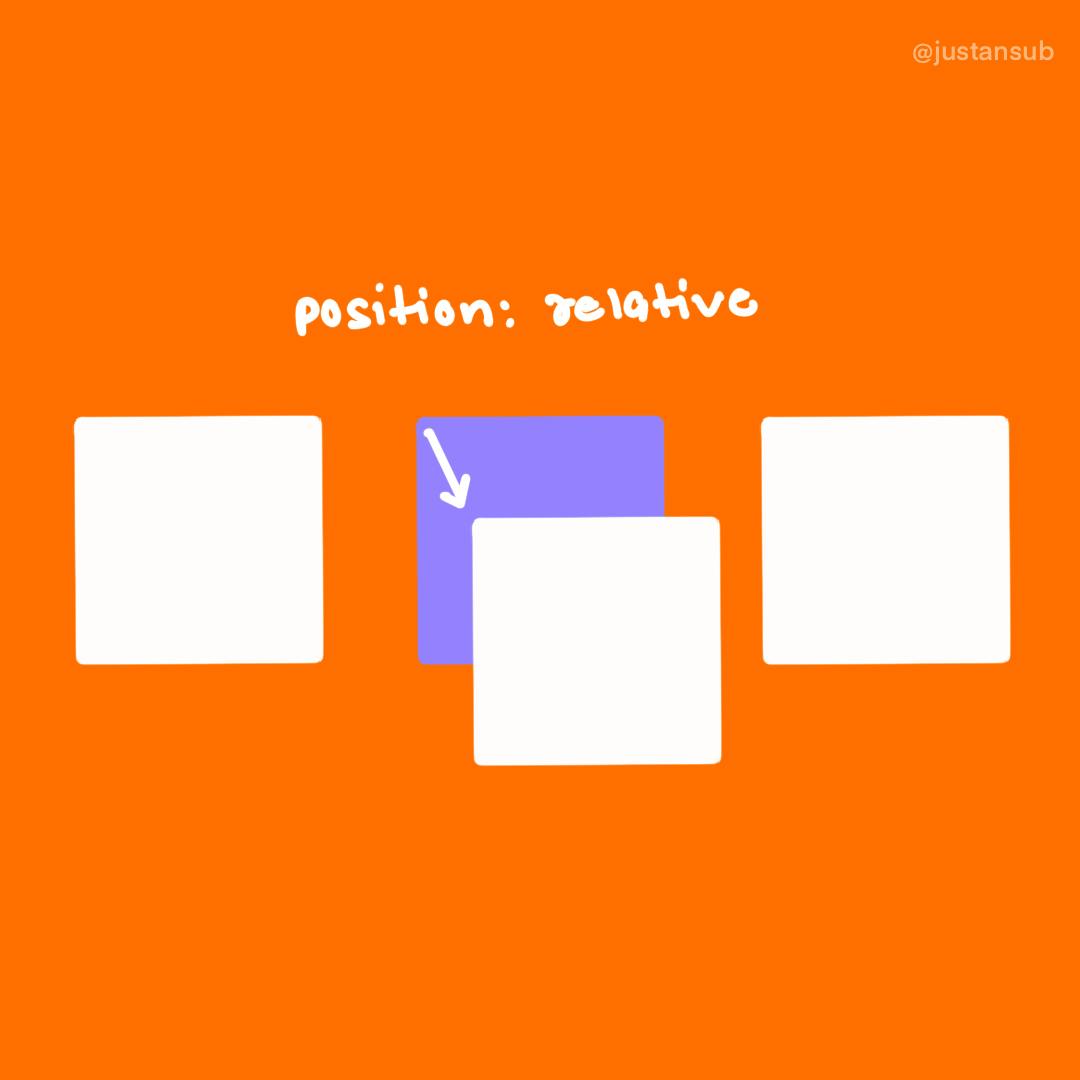
relative
- it helps us to change the location of the element relative to itself.
- for example:
<div class = "relative"> </div>
//CSS
.relative{
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
absolute
- this lets you place the element exactly where you want to put it.
- this changes the element according to its parent's element, and when there is no parent element, then it is going to change position according to the HTML element.
<div class = "absolute"> </div>
//CSS
.relative{
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}

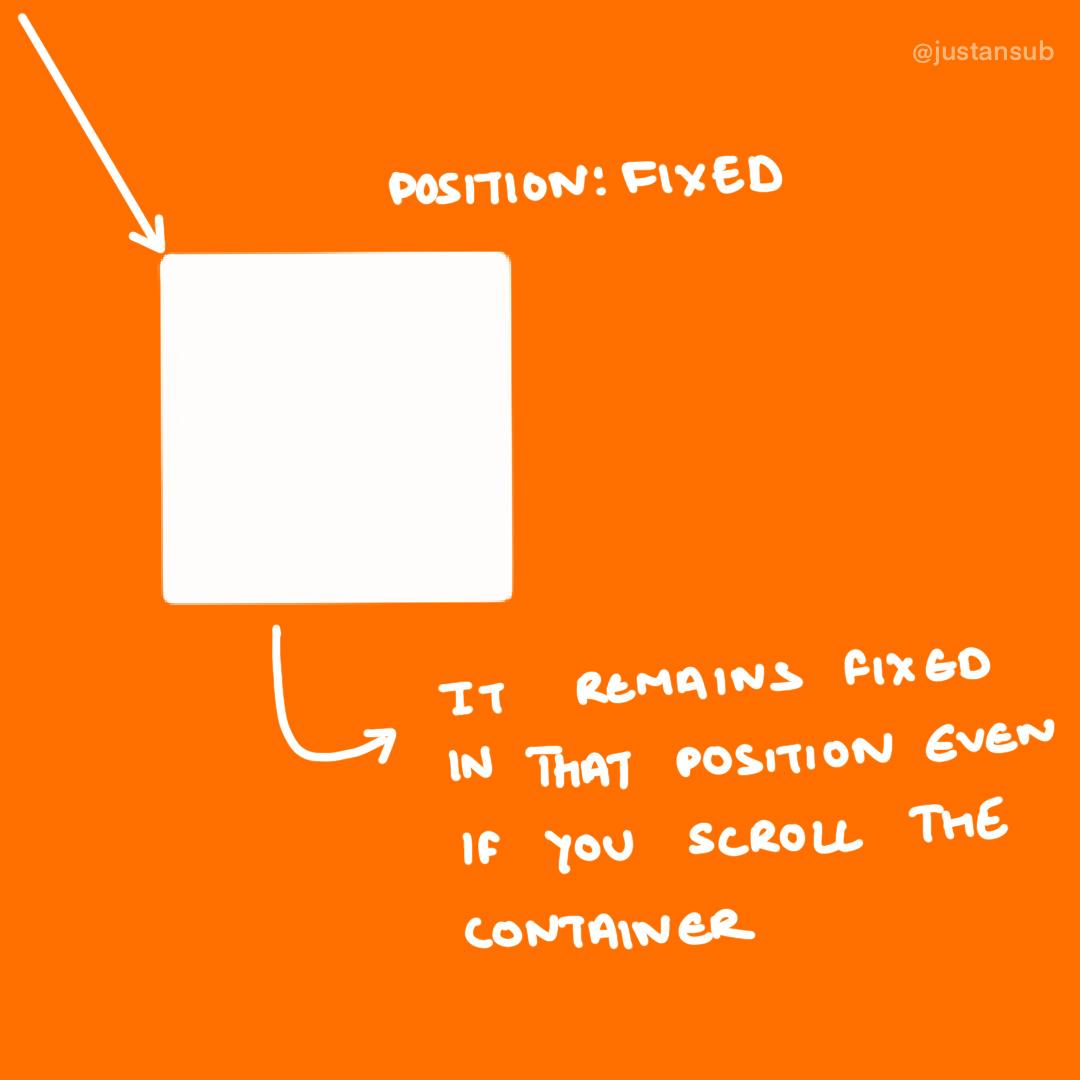
fixed
- position is going to fix even if you are going to scroll the webpage
- it is useful for fixed headers and footers
<div class="myDiv"></div>
.fixed{
position: fixed;
}
if you want any help with the positions of CSS or any other query then please contact me on my Twitter

